Bronchial irrigation with saline solution via a catheter passed through a rigid bronchoscope was first reported in 1927, and the term “bronchial lavage” was coined by Stitt in 1932. Although initially used as a therapy for septic lung disease or pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, lung lavage was subsequently employed to study lower respiratory tract immunity in various animal models in the 1960s and applied to the study of the human lung in the late 1960s and 1970s. A seminal article reporting the application of BAL to the study of secretions obtained from the human lung was published in 1974 when saline lavage of a portion of the lung via a flexible bronchoscope was introduced as a research tool by Reynolds and Newball . Saline lavage of a defined area of the lung became known as bronchoalveolar lavage, and hundreds of articles on BAL appeared in the literature in the 1980s and 1990s as clinical use of the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope expanded.
The technique rapidly gained acceptance, and a large number of centers began using the technique to obtain cells and proteins from the lower respiratory tract. However, many centers used their own technique for performing lavage, and concern arose that differences in technique could lead to significant differences in results obtained from BAL fluid analysis and the interpretation of such findings. Consequently, several groups established standardized methods for performing BAL. The European Respiratory Society has provided statements on the use of BAL for the clinical evaluation of patients with ILD including recommendations concerning the technical aspects of performing BAL and on standardization of the BAL procedure, and a multi-center, NIH-sponsored investigation conducted under the auspices of the American Thoracic Society in the United States examined BAL cell profiles in patients with ILD and normal volunteer subjects. Specific recommendations regarding various aspects of performing and analyzing BAL were subsequently published. However, these statements were published prior to the use of high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest as a routine clinical tool for the evaluation of patients with ILD and before the current classification of different forms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) had evolved to become the system that is currently accepted. Despite the promotion of BAL standardization in Europe, the technique has never been standardized on a global basis, and considerable variation in technique and in analysis persists among bronchoscopists and analytical laboratories around the world.
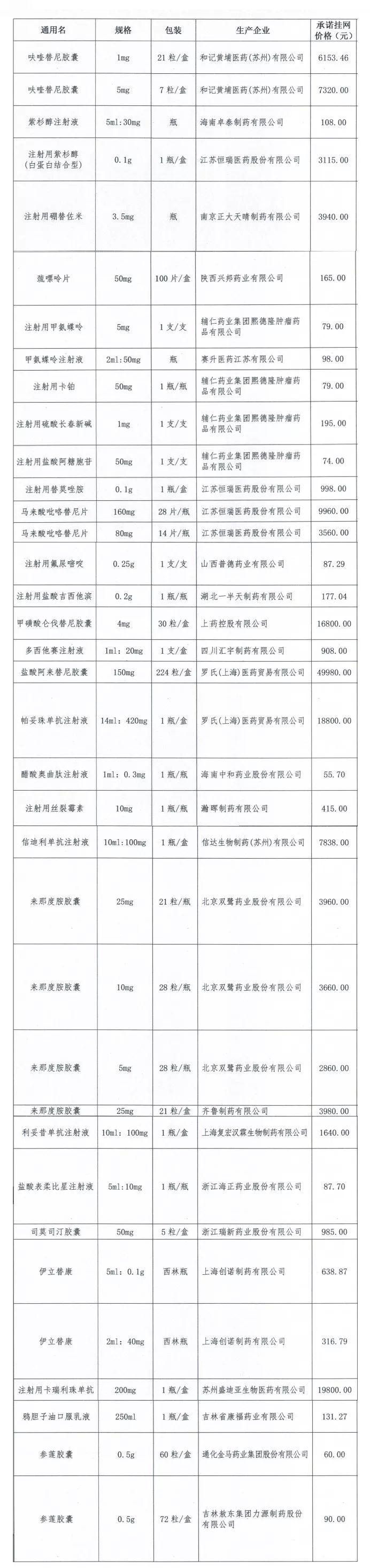
临床胸上段 2012年美国胸科学会临床实践攻略:支气管肺泡灌洗液细胞剖析在间质性肺病中的临床使用
精彩推荐
- 从单品爆款到产业标杆:解码尊界S800“百万级速度”背后的体系力量

2025年末,中国新能源汽车市场的竞争维度已然升华。当行业从粗放扩张步入品质为王的深水区,鸿蒙智行尊界S800的出现,如同一条跃出水面的巨鲸,不仅以现象级市场表现刷新了...详细
- 从产品聚合到命运共同体,鸿蒙智行构建全场景出行生态

2025年,鸿蒙智行迈入高质量发展的关键一年。全年交付量突破70万辆,同比增长接近60%,累计交付百万辆仅用43个月,较行业平均水平提速近20个月。在规模快速扩张的同时,产...详细
- 不看参数看体验:问界M5 Ultra与特斯拉Model Y怎么选?

在智能电动车的浪潮中,选择一台真正懂你、护你的出行伙伴,远比比较参数表更为重要。当问界新M5 Ultra与特斯拉Model Y同台竞技,我们看到的不仅是两款车的对决,更是两种...详细
- 尊界S800:用顶尖科技,保障冰雪路上的每一次安全

对于高端用户而言,冬季出行远非普通通勤可比。严寒低温、冰雪路面、续航缩短、座舱冰冷、操控风险等一系列季节性难题,不仅影响舒适与安全,更考验车辆的整体技术实力。尊...详细
本周热门
- 同仁堂健康双十一活动开启 “象食养医”倡导从健康的时候就关注健康

如果你想了解自己身体的秘密,让健康成为日常的生活方式,保持年轻的状态,实现抗衰老,逆生长的美好愿望,那么今年双十一的这场活动你一定不要错过。11月1日,同仁堂健康...详细