Over the past 3 decades, the prevalence of childhood obesity has increased dramatically in North America, ushering in a variety of health problems, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), which previously was not typically seen until much later in life. The rapid emergence of childhood T2DM poses challenges to many physicians who find themselves generally ill-equipped to treat adult diseases encountered in children. This clinical practice guideline was developed to provide evidence-based recommendations on managing 10- to 18-year-old patients in whom T2DM has been diagnosed. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) convened a Subcommittee on Management of T2DM in Children and Adolescents with the support of the American Diabetes Association, the Pediatric Endocrine Society, the American Academy of Family Physicians, and the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (formerly the American Dietetic Association). These groups collaborated to develop an evidence report that served as amajor source of information for these practice guideline recommendations. The guideline emphasizes the use of management modalities that have been shown to affect clinical outcomes in this pediatric population. Recommendations are made for situations in which either insulin or metformin is the preferred first-line treatment of children and adolescents with T2DM. The recommendations suggest integrating lifestyle modifications (ie, diet and exercise) in concert with medication rather than as an isolated initial treatment approach. Guidelines for frequency of monitoring hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and finger-stick blood glucose (BG) concentrations are presented. Decisions were made on the basis of a systematic grading of the quality of evidence and strength of recommendation.
The clinical practice guideline underwent peer review before it was approved by the AAP. This clinical practice guideline is not intended to replace clinical judgment or establish a protocol for the care of all children with T2DM, and its recommendations may not provide the only appropriate approach to the management of children with T2DM. Providers should consult experts trained in the care of children and adolescents with T2DM when treatment goals are not met or when therapy with insulin is initiated. The AAP acknowledges that some primary care clinicians may not be confident of their ability to successfully treat T2DM in a child because of the child’s age, coexisting conditions, and/or other concerns. At any point at which a clinician feels he or she is not adequately trained or is uncertain about treatment, a referral to a pediatric medical subspecialist should be made. If a diagnosis of T2DM is made by a pediatric medical subspecialist, the primary care clinician should develop a comanagement strategy with the subspecialist to ensure that the child continues to receive appropriate care consistent with a medical home model in which the pediatrician partners with parents to ensure that all health needs are met.
前期糖尿病的12大预兆 2013年美国AAP儿童青少年2型糖尿病攻略
精彩推荐
- 从品牌认知到价值共鸣:尊界以技术重定义豪华品牌成长范式

当中国新能源汽车市场从增量扩张转向存量深耕,一场关于品牌健康度的深层变革正在发生。杰兰路《2025年度下半年新能源汽车品牌健康度研究》指出:行业已跨越跑马圈地的阶段...详细
- 31.98万元起 “AI全场景家庭旗舰MPV”吉利银河V900开启预售

1月7日,吉利银河旗下V系列的首发之作,AI全场景家庭旗舰MPV吉利银河V900正式开启预售,共计3个版本,预售指导价格区间为31.98万元~38.98万元。新车围绕中国大家庭出行的真...详细
- 李氏医学探索带您重新认识移植威胁——BKPyV
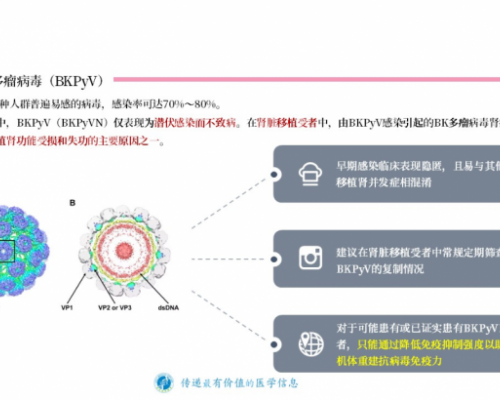
BK多瘤病毒(BKPyV)在人群中的感染率极高,研究显示可达70%80%。多数人在婴幼儿时期完成原发感染,随后病毒长期潜伏于泌尿系统上皮细胞内,在免疫功能正常的情况下几乎不...详细
- 李氏医学探索带你了解重性抑郁障碍,这一被忽视的“系统性疾病”

重性抑郁障碍(MDD)并不只是情绪低落那么简单。根据诊断标准,在同一两周内至少出现五项症状,并且必须包含持续的抑郁情绪或兴趣和愉悦感明显下降,才可能被诊断为 MDD。...详细
本周热门
- 同仁堂健康双十一活动开启 “象食养医”倡导从健康的时候就关注健康

如果你想了解自己身体的秘密,让健康成为日常的生活方式,保持年轻的状态,实现抗衰老,逆生长的美好愿望,那么今年双十一的这场活动你一定不要错过。11月1日,同仁堂健康...详细